normal end tidal co2 uk
The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. A normal trace appears as a series of rectangular waves in sequence with a numeric reading capnometry that shows the value of exhaled CO2.

Capnography Critical Care Practitioner
The researchers found that end-tidal CO2 could provide a highly sensitive predictor of return of spontaneous circulation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation MPR p791 Cantineau et al 1996.

. End-tidal CO2 monitoring is a non-invasive way to monitor a patients carbon dioxide levels. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor. During exhalation PAco2 continues to increase fig.
Both end-tidal CO2 monitors and pulse oximetry devices work closely together to help monitor the respiratory status of a patient. Understanding End Tidal CO 2 Monitoring. Levine RL Wayne MA Miller CC.
For a person with normal lungs the difference between end tidal and Paco2 can vary between 5-8mmHg depending on the book your reading. Trauma 2004 showed that end-tidal CO2 may be of value in predicting outcome from major trauma 19. Mean arterial PCO2 levels were 43241473 and mean ETCO2 levels were 34231086 mmHg.
The technique has been End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in neonates Carbon dioxide monitoring is vital in the management of ventilated newborn babies. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2 or mmHgThe normal values are 5 to 6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. Partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide successful predicts cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the field.
In patients with normal pulmonary function CO 2 normally 35 to 45 mm Hg and ETco 2 should correlate closely with a deviation of about 2 to 5 mm Hg. Agreement between PCO2 and ETCO2 measurements was 84 mmHg and a precision of 111 mmHgAs there is only a moderate correlation between PCO2 and ETCO2 levels in COPD patients ETCO2 measurement should not be considered as a part of the decision-making process to. A prospective observational study.
End-tidal and arterial carbon dioxide measurements correlate across all levels of physiologic dead space. The alveolar gas values determined at the end of an exhalation the end-tidal values are easy to measure but extremely difficult to interpret. Deakin et al.
Smith PB et al. Normal ETCO2 is in the range of 35 to 45 mmHg. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring is not as reliable as arterial.
On page 49 of the European Paediatric Advanced Life Support manual EPALS 4th edition there is a statement regarding end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 traces during CPR which states The absence of exhaled CO 2 during CPR does not guarantee tube misplacement. Since respiratory complications can be fatal it is essential that breathing is monitored constantly in high-risk patients. More recently a large group of medical doctors from several American hospitals tested over 100 patients and wrote an article End-tidal.
End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. So the short answer is you are right about the ranges 35-45 but that. 9 at a rate that is dependent on the mixed venous Pco2 Pnco2 value and to a level that depends on the duration of the.
Endtidal PO2 and PCO2. In hyperventilation the CO2 waveform becomes smaller and more frequent and the numeric reading falls below the normal range. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more.
Kolar M Krizmaric M Klemen P Grmec S. The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring or capnography End-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 monitoring is an attractive method as it is non-invasive portable and relatively inexpensive.
End tidal Co2 ranges vary slightly from actual PaCo2 and can be affected by many factors depending on the condition of the patients lungs. It measures End-tidal CO₂ which is the level of carbon dioxide exhaled at the end of a breath telling physicians how efficiently CO₂ is being carried through the blood back into the lungs and exhaled. Whilst this is technically correct particularly in a small child with a leak around a tracheal tube.
In a study of 191 blunt trauma patients only 5 of patients with an end-tidal CO2 determination of 325 kPa survived to discharge.
End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Easy Cap End Tidal Colorimetric Co2 Detector Reflex Medical

Co Monitoring And Capnometry Clinical View

How To Read And Interpret End Tidal Capnography Waveforms Emsuk Learning

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Concentration E Co2 Mm Hg For The Download Scientific Diagram
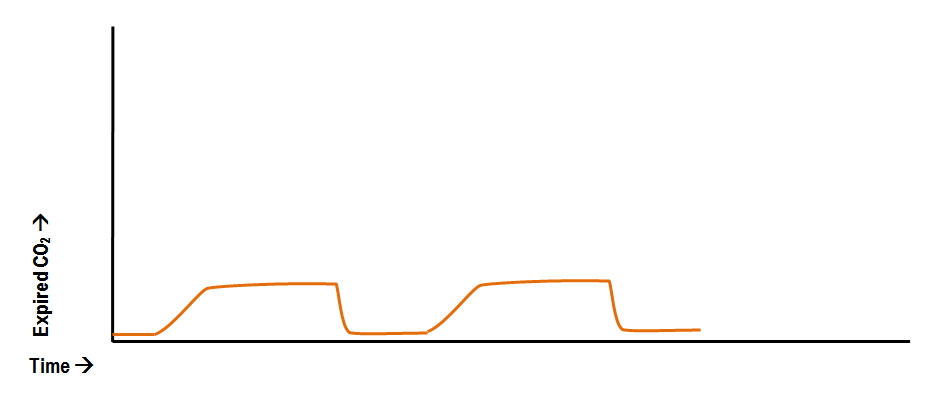
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology

Capnography Critical Care Practitioner

Capnography Critical Care Practitioner
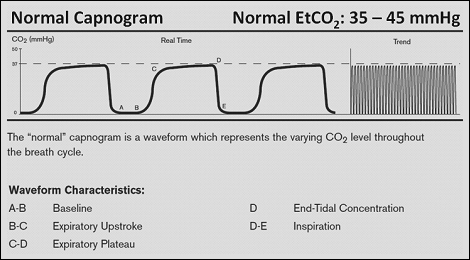
Capnogram R Series Defibrillator Zoll Medical Uk

Co Monitoring And Capnometry Clinical View

Figure 1 From Applications Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Monitoring In Emergency Department A Narrative Review Semantic Scholar

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

How To Read And Interpret End Tidal Capnography Waveforms Emsuk Learning

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram
